1.Brige Pattern
1.1 特徴
抽象と実装を独立して変更できるようにするために、抽象を実装から分離したDesign Patternです。1.2 目的
Bridgeパターンが解決する問題の説明の中に変更される「抽象と実装」が出てきます。 この抽象とは何か、実装とは何を指すのかを明確することに加えて、解決されている問題を分かりやすく説明する。1.3 抽象と実装の変更に伴う問題点
抽象クラスの変更の例として、ヒーター制御システム(Heater Controller)を考えます。以下の タイマー型とセンサー型のふたつの制御方式があるとします。- タイマー制御(Timer Model):タイマーでヒーターを一定時間オンにする時間型(Timer Model)
- センサー制御(Sensor Mode):温度センサーで温度を制御するセンサー型(Sensor Mode)
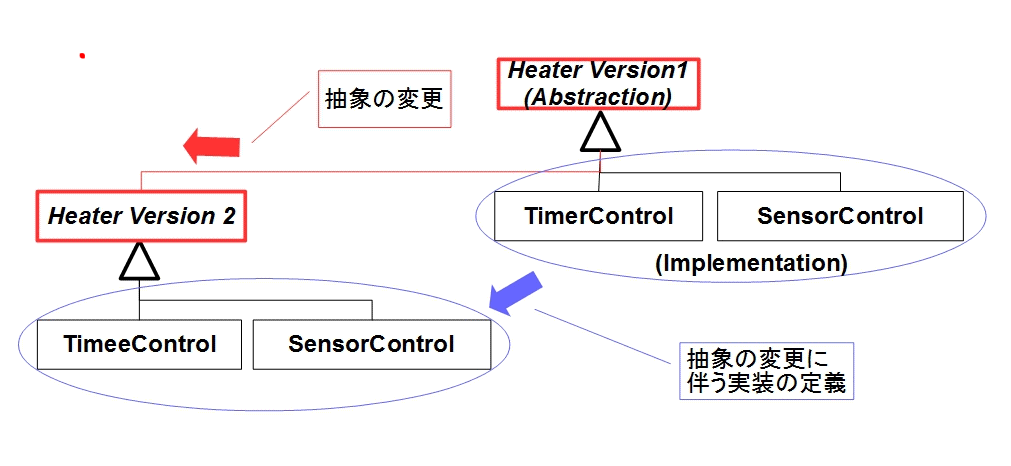
1.3 問題の解決
Bridgeパターンを用いるならば、「抽象クラスの継承では、実装クラスまでは継承されない」という 問題を橋(Bridge)をかけて解決できます。抽象クラス(Abstraction)は、インタフェースとなる
実装クラス(Implementor)への参照を保持して具体的な実装クラス(ConcreteImplementor)から操作を呼び出します。
そして、この抽象クラスを継承して修正された抽象クラス(RefinedAbstraction)が追加されます。
こうして、抽象クラスと実装クラス間の橋によって、あたかも抽象クラスがその実装クラスも継承しているかの
ようになります。
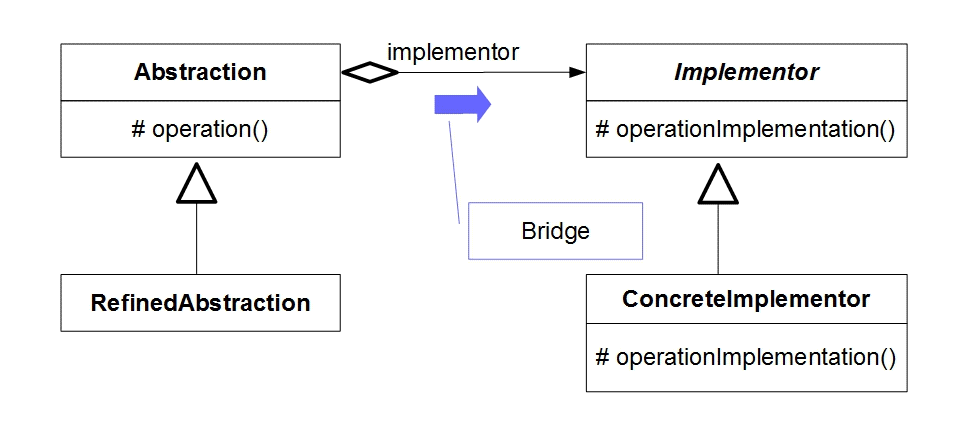
- Abstraction:抽象クラスのインターフェース
- RefinedAbstraction:抽象クラスの継承
- Implementor :実装クラスのインタフェース
- ConcreteImplementor :具体的な実装クラス
1.4 サンプルプログラム
Heater ControllerのVersion 2でシステム異常に対応して、Power Lampを点滅 させる機能が追加された。この場合、抽象クラスの修正のみで対応可能なことを 示す。修正箇所は赤で示した。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@protocol Implementor
- (void)powerLampOn;
- (void)powerLampOff;
@end
@interface TimerControl : NSObject<Implementor>
@end
@implementation TimerControl
- (void)powerLampOn;
{
printf("Timer Model Power Lamp On\n");
}
- (void)powerLampOff;
{
printf("Timer Model Power Lamp Off\n");
}
@end
@interface SensorControl : NSObject<Implementor>
@end
@implementation SensorControl
- (void)powerLampOn;
{
printf("Sensor Model Power Lamp On\n");
}
- (void)powerLampOff;
{
printf("Sensor Model Power Lamp Off\n");
}
- (void)powerLampblinkImplementationC;
{
printf(">\n");
}
@end
@interface Abstraction : NSObject
id<Implementor>_implementor;
- (id)initWithImplementor:(id<Implementor>)implementor;
- (void) powerLampblink;
@end
@implementation Abstraction
- (id)initWithImplementor:(id<Implementor>)implementor
{
if (self = [super init]) {
_implementor = implementor;
}
return self;
}
- (void) powerLampblink
{
printf("must override powerLampblink method of subclass.");
}
@end
@interface Version1 : Abstraction
- (id)initWithImplementor:(id<Implementor>)implementor;
- (void) powerLampblink;
@end
@implementation Version1
- (id)initWithImplementor:(id<Implementor>)implementor
{
self = [super initWithImplementor:implementor];
return self;
}
- (void) powerLampblink
{
printf("Nothing to control the power lamp.\n");
}
@end
@interface Version2 : Abstraction
- (id)initWithImplementor:(id<Implementor>)implementor;
- (void) powerLampblink;
@end
@implementation Version2
- (id)initWithImplementor:(id<Implementor>)implementor
{
self = [super initWithImplementor:implementor];
return self;
}
- (void) powerLampblink
{
[_implementor powerLampOn];
[_implementor powerLampOff];
[_implementor powerLampOn];
[_implementor powerLampOff];
}
@end
@interface Client : NSObject
- (void)execute;
@end
@implementation Client
- (void)execute
{
id<Implementor> timer = [[[TimerControl alloc] init] autorelease];
Version1 *timerVersion1;
Version2 *timweVersion2;
printf("-- Timer Control Version 1 Blink Test --\n");
timerVersion1 = [[[Version1 alloc] initWithImplementor:timer] autorelease];
[timerVersion1 powerLampblink];
printf("\n-- Timer Control Version 2 Blink Test --\n");
timweVersion2 = [[[Version2 alloc] initWithImplementor:timer] autorelease];
[timweVersion2 powerLampblink];
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
Client *client;
client = [[[Client alloc] init] autorelease];
[client execute];
[pool drain];
return 0;
}
参考文献: Deign Pattern by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides